WHAT IS DATA SECURITY?
In recent years with emerging cloud technologies, security threats over data are constantly rising. Whether you run your application in private, public or hybrid infrastructure. Integrations with different parties or using software as service (Saas), data flowing in different directions within the set at some point touches cloud storage.
In recent years with emerging cloud technologies, security threats over data are constantly rising. Whether you run your application in private, public or hybrid infrastructure. Integrations with different parties or using software as service (Saas), data flowing in different directions within the set at some point touches cloud storage.
With more and more companies adopting to cloud storage/services, providing data security is becoming pinnacle of importance due to the following reasons:
- Third party hosting limits visibility of data storage.
- In case of multiple cloud providers involved may lead to inconsistent security protocols.
- Compliance with regulations.
- Shared security responsibilities misunderstood.
- Exposure to data leaks.
HOW DATA SECURITY WORKS?
Data security protocols are ever-evolving but adopting basic best practices decreases complexity significantly.
1. Understanding your responsibility
Hosting and managing applications on in-premise infrastructure makes companies sole responsible of data security. But in cloud, things get much more complicated. With integrations companies assume certain aspects of IT-security to be taken care by cloud provider and vice-versa. It’s important to have clear idea of responsibilities shared between both parties. Security professionals call this shared responsibility model.
Leading cloud providers viz. Amazon, Microsoft, Google provide documentations so all parties understand responsibilities accordingly to deployments. Following is responsibility shared by AWS
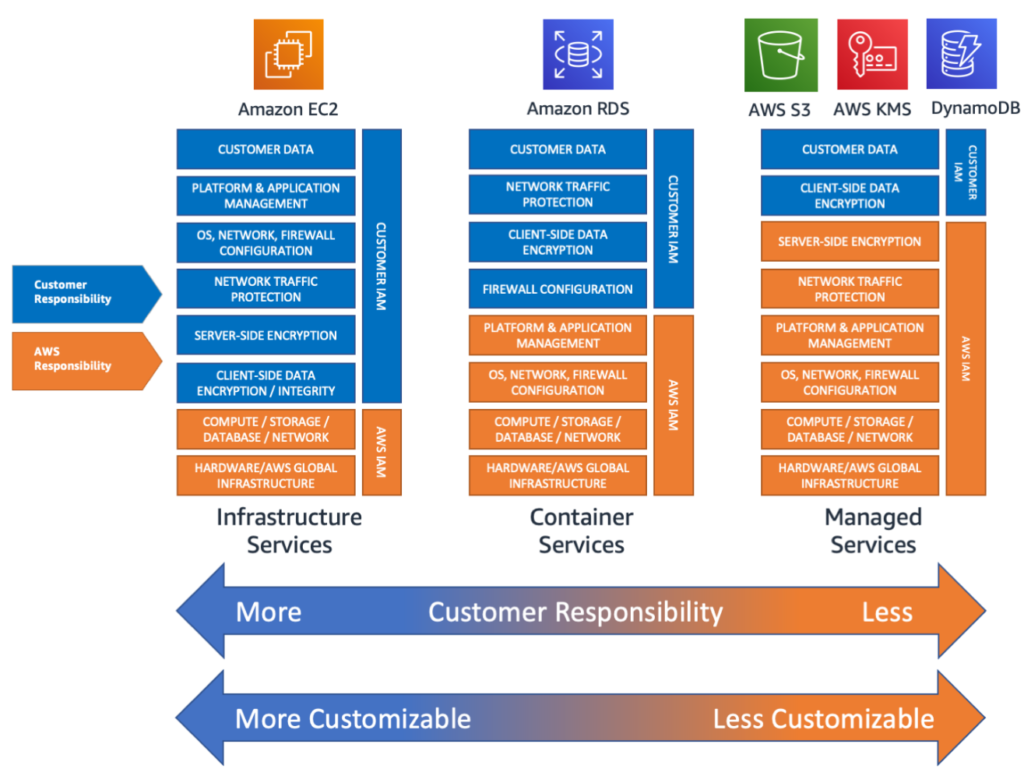
In addition to understanding responsibility companies should ask detailed security questions viz. geographical locations where data is saved, disaster recovery plan, authentication methods provided etc.
2.Equip your resources
DevOps and developers are the building blocks while implementing any applications. Educating them provides backbone of security through and through. Comprehensive training should include basic security knowledge like using strong passwords and identify possible attack scenarios.
Most importantly training should help resources understand sensitivity and risk of data leakage. And it’s monetary impact on business.
3. Securing Endpoints
Cloud service use intensifies need for strong end point security. Endpoint detection and response (EDR) tools and/or endpoint protection platforms (EPP) can help in this area. EDR and EPP solutions combine traditional endpoint security capabilities with continuous monitoring and automated response. Specifically, these tools address a number of security requirements, including patch management, endpoint encryption, VPNs, and insider threat prevention among others. Along with it unused non secure ports should be blocked.
Conclusion
You never know when a stealthy hacker could attack your business and make you go under. All organizations, independent of their size, can benefit from these best practices and improve their cloud usage security.
