
Graph databases are well-suited for analyzing interconnections between data points in data fabric which has created a lot of interest in using graph databases. Graph databases are best suited for working with data in business disciplines that involve complex relationships and dynamic schema.
What is GraphDb?
It’s all based on the branch of mathematics called Graph (Discrete Mathematics).
Graph databases are based on semantic data models. These databases connect specific data points (nodes) using relationships (edges) in the form of graphs that can then be retrieved by the user using queries.
Graph is a way of writing data to a database along with additional information so as to solve complex analytical problems. It can be visualized as a web or a network.
Writing data as a graph requires 3 main components – Noun(Vertex/Node), Verb(Edge/Relationship) and their properties. As Nodes and their Relationships are explicitly written into the data, it makes it quicker to identify the connections between two Nodes.
How different is it from relational databases?
In traditional Relational Databases the data is joined on Read. Querying relationships can take a long time as these are implemented with foreign keys and queried by joining tables. Relational databases are designed to answer known questions.
But in graph databases the data is joined on Write, that is, the relationships are stored along with the data in a native way. Hence they are designed to answer questions which we didn’t know were going to be posed when the data was gathered. This paradigm shift helps in answering “How is the data connected?” using GraphDB, rather than “Is my data connected?” as with Relational Databases. This helps us in deriving valuable insights from the data points efficiently, quickly and easily.
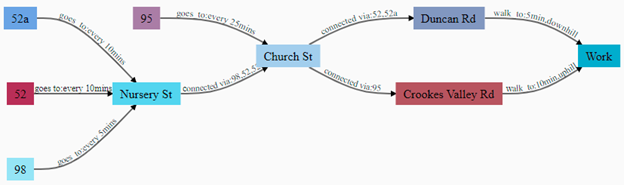
The above shown subset of transport routes data is created with the relationships. It enables easier querying to get the desired results. It is similar in many ways to the way our brain stores information and the interconnections between information. It can answer questions like how to get to Work from Nursery St, and also get the shortest path, or less time consuming path. If Users Data is added to the Routes Data then It helps find patterns of connection in data, like how often a user chooses a particular route, giving insights on how to improve the effectiveness of the routes. Such insights help predict user behavior, improve the business and streamline the revenue generation contributing to overall business growth.
Where should I use?
GraphDB is used in scenarios where data is highly connected and the goal is to capture the complex relationships in the vastness of it. In a gist, it’s recommended where the Relationship between data is more important than the data itself.
In one of our use cases we looked at data on Patients for diseases analysis. We initiated our modeling exercise with family relationship, and then medical history. The insights were not that distinct, but we further changed the model to inject location node that resulted in completely new insights. This showed that we could change the model frequently unlike relationship database to project the data based on the questions asked instead constraining one-self with relationship embedded in table structure. There are many more aspects of GraphDB which we will continue discussing in this blog series.
Start your journey into Graph db by engaging with our in-house professionals. Write to us : prismatic@prissoft.net
– By Gayathri Bhave
